NH Snow Cover Extent
| December 2014 | Snow Cover Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (49 years) | Record | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||
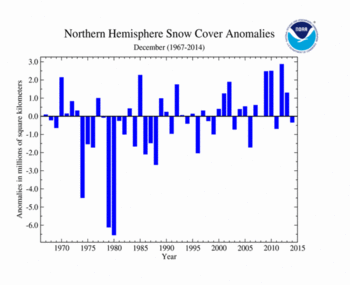
| Northern Hemisphere | 43.65 | 16.85 | -0.62 | -0.24 | +0.41 | +0.16 | Largest | 30th | 2012 | 46.85 | 18.09 |
| Smallest | 20th | 1980 | 37.44 | 14.46 | |||||||
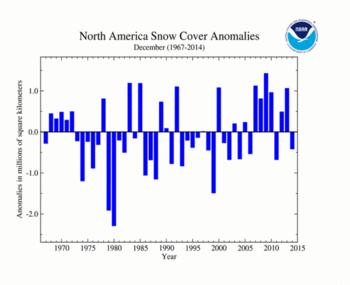
| North America | 16.43 | 6.34 | -0.47 | -0.18 | +0.12 | +0.05 | Largest | 32nd | 2009 | 18.27 | 7.05 |
| Smallest | 18th | 1980 | 14.56 | 5.62 | |||||||
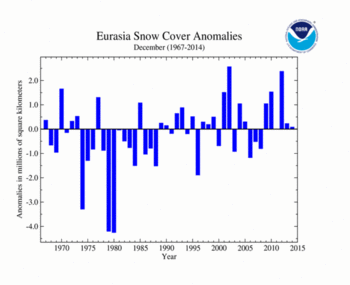
| Eurasia | 27.22 | 10.51 | -0.14 | -0.05 | +0.29 | +0.11 | Largest | 23rd | 2002 | 29.70 | 11.47 |
| Smallest | 27th | 1980 | 22.88 | 8.83 | |||||||
Data Source: Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University. Period of record: 1966–2014 (49 years)
The Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent (SCE) during December was 43.65 million square km (16.85 million square miles), 330,000 square km (130,000 square miles) below the 1981-2010 average. This was the 20th smallest December SCE in the 49-year period of record for the Northern Hemisphere. The North American December SCE was slightly below average, while the Eurasian December SCE was slightly above average.
During December, the North American SCE was slightly below average, the 25th smallest December SCE on record. The monthly SCE was 16.43 million square km (6.34 million square miles), 420,000 square km (170,000 square miles) below average. This was the smallest December SCE for North America since 2011. The entire contiguous U.S. was warmer than average, limiting snow cover there. The contiguous U.S. had its 14th smallest December SCE. Canada had its 16th largest December SCE. Above-average SCE was observed across the Great Plains and northeastern U.S., the Canadian Rockies, and north of the Great Lakes. Below-average SCE was observed in the western and midwestern United States.
The Eurasian December SCE was 27.22 million square km (10.51 million square miles), 90,000 square km (40,000 square miles) above average and the 23rd largest December SCE for Eurasia. Below-average snow cover was observed across much of western Europe, northern China, and Mongolia. Above-average snow cover was observed across eastern Europe, Kazakhstan, and central China.
Sea Ice Extent
| December 2014 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (36 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
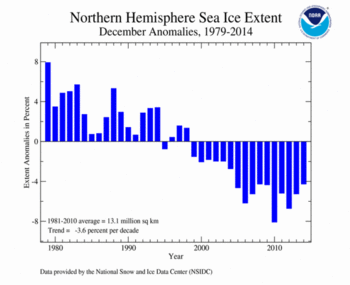
| Northern Hemisphere | 12.35 | 4.77 | -0.40% | -3.55% | Largest | 27th | 1982 | 13.64 | 5.27 |
| Smallest | 9th | 2010 | 11.83 | 4.57 | |||||
| Southern Hemisphere | 11.93 | 4.61 | +14.71% | +3.27% | Largest | 2nd | 2007 | 11.98 | 4.63 |
| Smallest | 34th | 1982 | 9.22 | 3.56 | |||||
| Globe | 24.28 | 9.37 | +6.44% | -0.44% | Largest | 3rd | 1988 | 24.69 | 9.53 |
| Smallest | 33rd | 2006 | 21.80 | 8.42 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2014 (36 years)
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent — which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites — averaged for December 2014 was 12.52 million square km (4.83 million square miles), 540,000 square km (210,000 square miles), or 4.1 percent, below the 1981-2010 average. This was the ninth smallest December sea ice extent on record for the Arctic, but the largest since 2008. The Arctic gained about 2.00 million square km (772,000 square miles) of ice during December, which is near the 1981-2010 average. The smallest December Arctic sea ice extent occurred in 2010 at 12.02 million square km (4.64 million square miles). Sea ice coverage was below average in the Bering Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk. Near-average sea ice was observed across the Atlantic side of the Arctic, particularly the Kara and Barents Seas — both of which have had much below-average ice cover over the past several winters. December Arctic ice extent is decreasing at an average rate of 3.5 percent per decade.
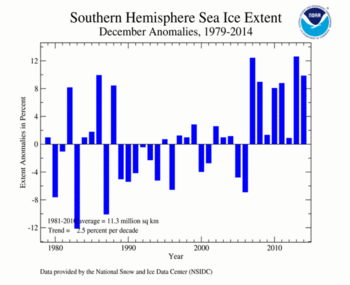
The December Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was 12.38 million square km (4.78 million square miles), which was 1.11 million square km (430,000 square miles), or 9.9 percent, above the 1981-2010 average. This was the fourth largest December Antarctic sea ice extent on record. The largest December Antarctic sea ice occurred in 2013, and was about 310,000 square km (120,000 square miles) larger than the December 2014 sea ice extent. Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent is increasing at an average rate of 2.6 percent per decade.
When combining the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere sea ice extents, the globally-averaged sea ice extent during December was 24.90 million square km (9.61 million square miles), 2.3 percent above the 1981-2010 average, and the sixth largest December global sea ice extent on record. December global sea ice extent is declining at an average rate of 0.6 percent per decade.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information