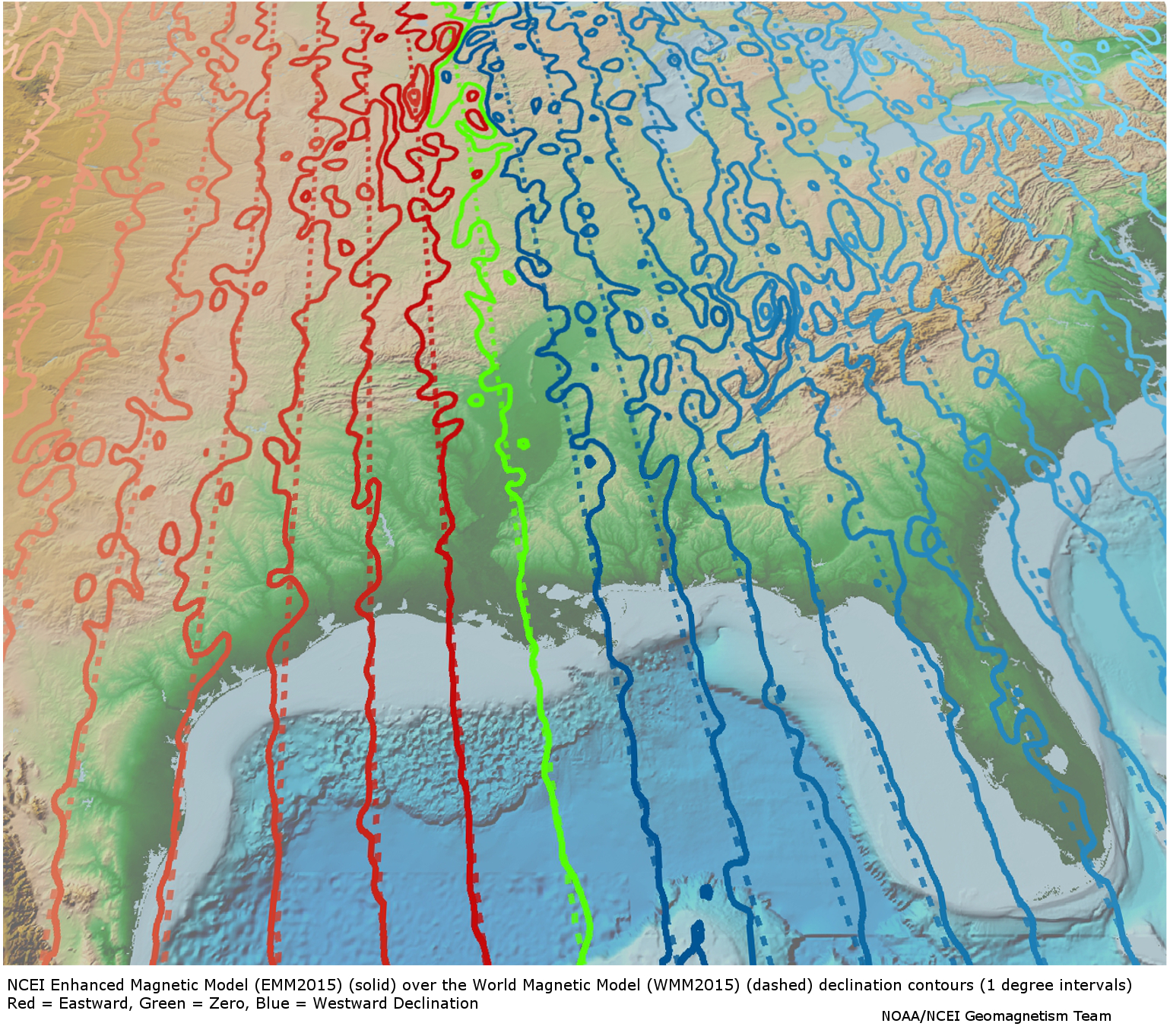
Enhanced Magnetic Model 2015
The Enhanced Magnetic Model (EMM) extends to degree and order 720, resolving magnetic anomalies down to 56 km wavelength. The higher resolution of the EMM results in significantly improved pointing accuracy than the World Magnetic Model (WMM), which uses spherical harmonic representation to degree and order 12, resolving the magnetic field at 3000 km wavelength. The EMM model provides the magnetic field vector at any desired location and altitude close to and above the Earth's surface.
- Cite as: Chulliat, A.. P. Alken. Nair, A. Woods. S. Maus. 2015: Enhanced Magnetic Model 2015. 1. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. https://doi.org/10.7289/V56971HV. Accessed [date].
- doi:10.7289/V56971HV
- NCEI Metadata ID: gov.noaa.ngdc.mgg.geophysical_models:EMM2015
gov.noaa.ngdc.mgg.geophysical_models:EMM2015
| Download Data |
|
| Distribution Formats |
|
| Ordering Instructions | Contact NCEI for other distribution options and instructions. |
| Distributor | NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information
ncei.info@noaa.gov |
| Dataset Point of Contact | NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information
ncei.info@noaa.gov |
| Dataset Point of Contact | NCEI Geomagnetic Modeling Team
NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information geomag.models@noaa.gov |
| Time Period | 2000-01-01 to 2019-12-31 |
| Spatial Reference System | urn:ogc:def:crs:EPSG::4326 |
| Spatial Bounding Box Coordinates |
N: 90
S: -90
E: 180
W: -180
|
| Spatial Coverage Map | |
| General Documentation | |
| Publication Dates |
|
| Edition | 1 |
| Data Presentation Form | mapDigital
|
| Dataset Progress Status | Complete - production of the data has been completed
Historical archive - data has been stored in an offline storage facility |
| Data Update Frequency | As needed |
| Purpose | Magnetic anomaly maps provide insight into the subsurface structure and composition of the Earth's crust. Over continental areas, magnetic anomalies illuminate geologic, tectonic, and geothermal evolution of crust and lithosphere. In the world's oceans, anomalies trending parallel to the isochrons (lines of equal age) reveal the temporal evolution of oceanic crust. Magnetic maps are widely used in the geological sciences and in resource exploration. |
| Use Limitations |
|
| Dataset Citation |
|
| Cited Authors |
|
| Originators |
|
| Publishers |
|
| Theme keywords | Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Science Keywords
|
| Data Center keywords | Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Data Center Keywords
|
| Place keywords | Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Location Keywords
|
| Use Constraints |
|
| Access Constraints |
|
| Other Constraints | Cite as: Chulliat, A.. P. Alken. Nair, A. Woods. S. Maus. 2015: Enhanced Magnetic Model 2015. 1. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. https://doi.org/10.7289/V56971HV. Accessed [date]. |
| Fees |
|
| Processor |
|
| Processing Steps |
|
| Source Datasets |
|
| Processing Steps |
|
Last Modified: 2020-05-14
For questions about the information on this page, please email: ncei.info@noaa.gov